Overview
Sharkie is a desktop expense tracker application. The user interacts with it using a CLI, and it has a GUI created with JavaFX. It is written in Java, and has about 10 kLoC.
Summary of contributions
-
Major enhancement:
-
Added
lendcommand (Pull request #87)-
What it does: Allows the user to record the amount of money lent to other people in Sharkie’s contact list.
-
Justification: This is one of the key features of Sharkie, which records the flow of money between the user and the people in Sharkie.
-
Highlights: This command involves both
TransactionsandPersonmodels, considerations have to made on how to use both of the models without changing their purposes or properties.
-
-
Added
receivedcommand (Pull request #98)-
What it does: Allows the user to record that a person, who the user lent to has returned the amount of money.
-
Justification: This is an essential update, which allows the user to remove the
loansrecorded by thelendcommand. -
Highlights: Considerations were needed during the implementation of this feature, to preserve the immutable property of
Person.
-
-
Added user data storage (Pull request #95)
-
What it does: Stores user data, such as name, phone and e-mail address.
-
Justification: The storage of user data is important, as the user details are required during the use of
remindandremindallcommands. -
Highlights: This update was challenging, an entire new storage need to be built to store the user data, as the data needed to be stored differs from those in the address book.
-
-
Added
remindandremindallcommand (Pull request #95)-
What it does: Allows the user to send reminders to the people, who have not return the amount of money they lent, via email.
-
Justification: This is one of the main features of Sharkie, which allows the interaction between the user and the people in Sharkie’s contact list.
-
Highlights: The implementation of this feature was new to me, as it involves the usage of the internet and the connection to e-mail servers.
-
Credits: javax.mail is used in the implementation of this feature.
-
-
-
Minor enhancement:
-
Make Sharkie sends a confirmation email to user to validate the user’s email address during user’s first login. (Pull request #249)
-
-
Code contributed: [Functional codes & Test codes]
-
Other contributions:
-
Enhancements to existing features:
-
Add progress indicator for command execution, to indicate that the application is not hanging during execution of commands, which take some time to run, such as
people remind. (Pull request #148) -
Improved GUI of Edit User Data Window and Help Window. (Pull request #178)
-
Made
people’s tagsuneditable. (Pull request #183)
-
-
Project management:
-
Finalized and tagged
v1.1-v1.4(4 versions) on Github. -
Managed release of
v1.2.1-v1.4(3 releases) on Github.
-
-
Documentation:
-
Updated the product website’s heading and navigation bar. (Pull requests #44, #81)
-
Edited About, Features, Commands and FAQ sections of the User Guide. (Pull requests #49, #192)
-
Added use cases in the appendix. Updated Design, Implementation and Manual Testing sections of the Developer Guide. (Pull requests #51, #132, #134, #146 #192, #200)
-
-
Community:
-
Contributions to the User Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the User Guide. They showcase my ability to write documentation targeting end-users. |
About
This user guide will help to ensure that you have all the information you need to utilise Sharkie to its fullest extent. Sharkie is a feature-filled expense tracker and all the information you need regarding its usage is available below.
If you need help starting up Sharkie, you can head on to Quick Start below to set it up.
If you want to find out more about the features provided by Sharkie, you can visit Features below.
If you need help regarding what commands Sharkie has, Commands below will guide you through Sharkie’s commands.
Note the following symbols and formatting used in this document:
Symbol/ |
Meaning |
|
A grey highlight (called a mark-up) indicates that this is a command that can be typed into the command line and executed by the application. |
Enter |
This symbol indicates the enter button on the keyboard. |
This yellow box indicates the restrictions of each command. |
|
|
This symbol indicates warnings to take note of. |
|
This symbol indicates information that you need to know. |
|
This symbol indicates tips that can help you in your use of Sharkie. |
Features
Expenditure and Income
If you are a university student who has started to manage your own money, but struggles to track your expenses or meet your saving goals, Sharkie would be a good application for you to start with.
Sharkie allows you to record what you have spent on for the month, and also notes down your income for the month to help you properly track your money flow!
| You may visit [wallet-commands] to find out more on how to record expenses or incomes in Sharkie. |
Commands
Adding a person: add
Suppose you want to add a new person to the contact list, the command you would enter is our people add command.
Format: people add n/<name> p/<phone number> e/<email address>
Command Format
The following are the restrictions of people add command, which you would need to take note of:
-
The
<name>you entered should only contain alphanumeric characters and spaces. -
The
<phone number>you entered should only contain numbers and it should be at least 3 digits long. -
The
<email address>you entered should be in the format of local-part@domain.-
The local-part should only contain alphanumeric characters and these special characters, excluding the parentheses (!#$%&'*+/=?`{|}~^.-).
-
The domain name must be at least 2 characters long, start and end with alphanumeric characters.
-
Example:
-
Suppose you want to add your new friend, "Joel", along with his phone number "91234567" and email "joel@example.com" into the contact list.
-
The command you would enter is
people add n/Joel p/91234567 e/joel@example.com. -
This adds a person named "Joel" into your contact, along with his phone number and e-mail address.
-
Expected Outcome:
-
Your new friend, "Joel" will be added into your contact list:
New person added: Joel Phone: 91234567 Email: joel@example.com You owe: $0.00 You lent: $0.00
Recording the money you received: received
Suppose you want to record that you have received the money for a certain loan (or for all loans) from your friend,
the command you would enter is our people received command.
Format: people received <person’s index> [i/<loan’s index>]
Command Format
The following is the restrictions of people received command, which you would need to take note of:
-
The
<person’s index>and<loan’s index>you entered should be positive integers, e.g. 1, 2, 3, …
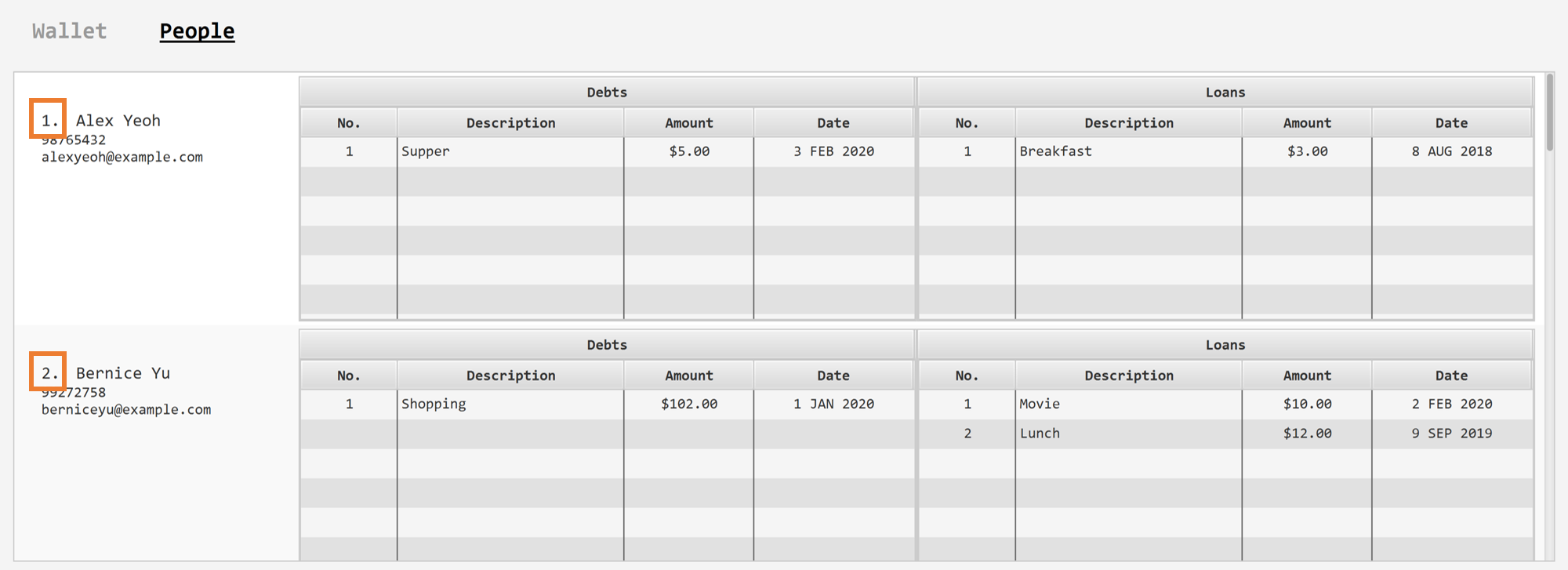
The <person’s index> above refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list in Sharkie. It indicates a
specific person in the contact list, who you received from.Still confused? Find out more about what is a person’s index. The <loan’s index> above refers to the index number shown in the displayed loans list in Sharkie. It indicates a
specific loan under the person, which you received from.Still confused? Find out more about what is a loan’s index. Loans represent the amount of money you lend your friends. Still confused? Find out more about the differences between debts and loans. |
The <loan’s index> is optional.
All loans will be removed for the indicated person if the <loan’s index> is not specified.
|
Example:
-
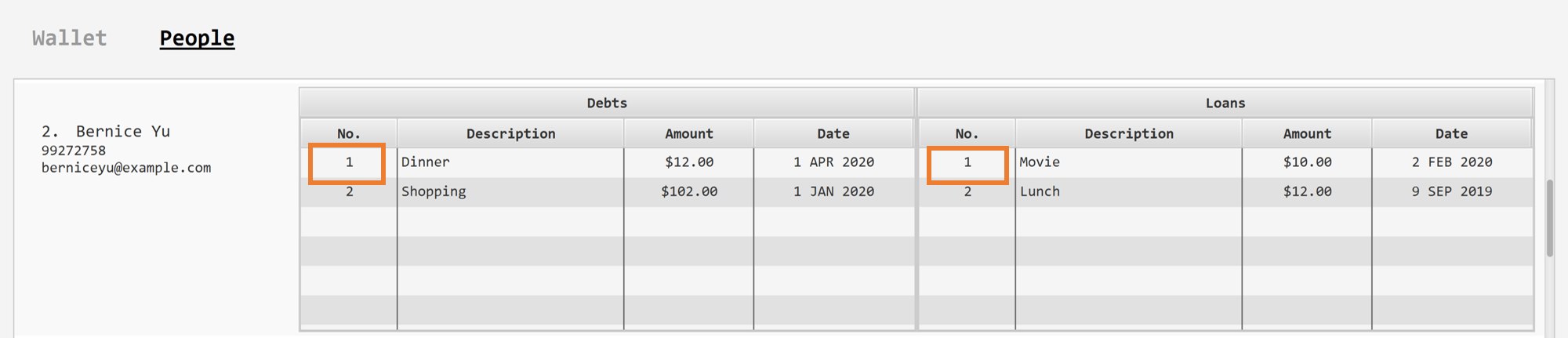
Suppose you want to record that you have received the money from "Joel", who is the second person in the contact list, for the first loan in his loans list.
-
The command you would enter is
people received 2 i/1. -
This records that you have received the money for the first loan of "Joel", the second person in the contact list.
-
Expected Outcome:
-
The first loan of "Joel" will be removed from his loans list and the unsettled loans of "Joel" will be shown.
Removed loan to Joel by $10.00. Joel now owes you $2.00.
Sending reminder to a friend: remind
Suppose you want to remind a friend to return unsettled loans to you through an email,
the command you would enter is our people remind command.
Format: people remind <person’s index>
Command Format
The following are the restrictions of people remind command, which you would need to take note of:
-
The
<person’s index>you entered should be a positive integer, e.g. 1, 2, 3, …
|
You would need to connect to the Internet and include your details in Sharkie before using this command.
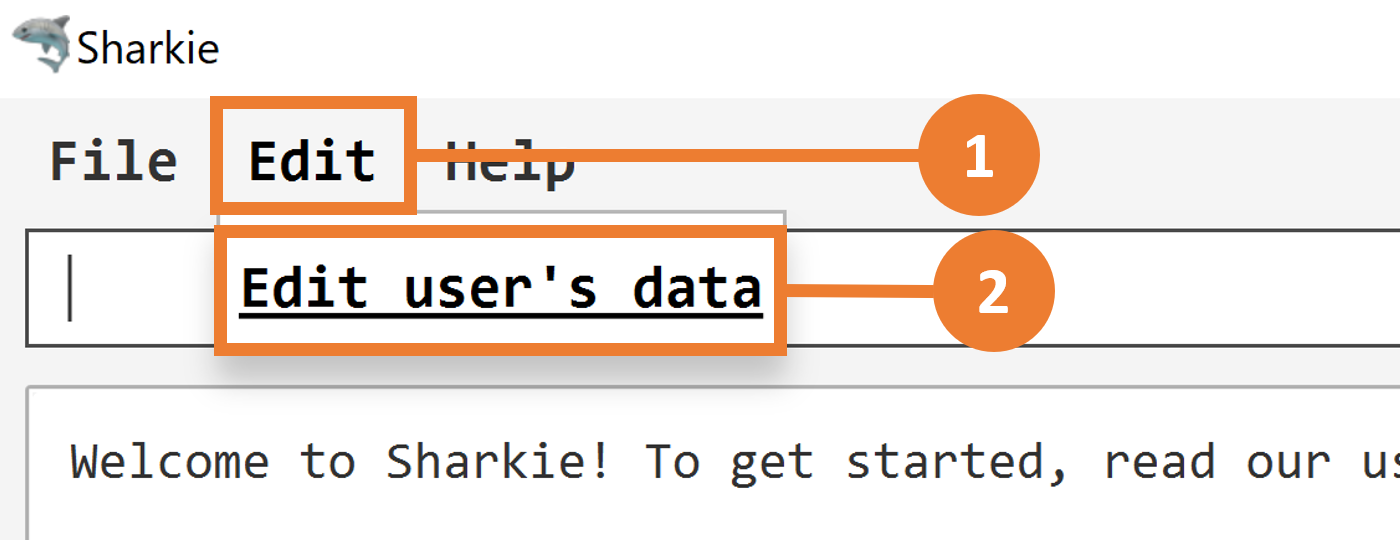
You can enter or edit your details at "Edit" > "Edit user’s data". Before you enter the people remind command, please make sure that your friend’s email address is correct.
|
The <person’s index> above refers to the index number shown in the displayed person list in Sharkie. It indicates a
specific person in the contact list, who you want to remind.Still confused? Find out more about what is a person’s index. Loans represent the amount of money you lend your friends. Still confused? Find out more about the differences between debts and loans. |
If you receive connection error messages during the execution of the people remind command,
please visit how to resolve connection issues.
|
Example:
-
Suppose you want to remind "Daniel", who is the first person in your contact list to return you your money.
-
The command you would enter is
people remind 1. -
This requests Sharkie to send an email to "Daniel", the first person in your contact list.
-
Expected Outcome:
-
"Daniel" will receive a reminder from Sharkie via his email. You will also receive a carbon copy (CC) of the email sent to "Daniel":
Reminded Daniel to return $3.00! Sharkie has sent a carbon copy (CC) of the reminder to your email!
Sending reminder to all friends: remindall
Suppose you want to remind all your friends in your contact list to return you your money,
the command you would enter is our people remindall command.
Format: people remindall
|
You would need to connect to the Internet and include your details in Sharkie before using this command.
You can enter or edit your details at "Edit" > "Edit user’s data". Before you enter the people remindall command, please make sure that your friends' email addresses are correct.
|
|
Only your friends, who have unsettled loan(s) will be reminded. Your friends who have zero loans will
not receive a reminder. Loans represent the amount of money you lend your friends. Still confused? Find out more about the differences between debts and loans. |
If you receive connection error messages during the execution of people remindall command,
please visit how to resolve connection issues.
|
Example:
-
Suppose you want to remind all your friends in your contact list who have yet to repay you.
-
The command you would enter is
people remindall. -
This requests Sharkie to send an email to everyone in your contact list who have yet to repay you.
-
Expected Outcome:
-
All your friends who have yet to repay you will receive a reminder from Sharkie via their emails. You will also receive a carbon copy (CC) of each of the emails sent to your friends:
Reminded Cheyanne to return $20.00! Reminded Daniel to return $10.00! Reminded Joel to return $30.75! Sharkie has sent carbon copies (CC) of the reminders to your email!
Finding a person: find
Suppose you want to find a person in your contact list by a specific keyword,
the command you would enter is our people find command.
Format: people find n/<keyword> [<keyword>…]
or people find p/<keyword> [<keyword>…]
or people find e/<keyword> [<keyword>…]
or people find t/<keyword> [<keyword>…]
Command Format
The following are the restrictions of people find command, which you would need to take note of:
-
You would not have to consider the case of the
<keyword>, as it is case-insensitive. -
The
<keyword>you want to enter can be incomplete. For example,people find n/jowill display the persons whose name contains the keyword "jo", such as "Joel". -
The
<keyword>you entered should be one of the prefixes: name (n/), phone (p/), email (p/) or tag (t/).-
You may use the tag prefix
t/to find people with debts or loans in your contact list. Hence,DebtandLoan(case-insensitive) are the only tags, which you are allowed to use inpeople findcommand.
-
|
Debts represent the amount of money you owe your friends and
loans represent the amount of money you lend your friends. Still confused? Find out more about the differences between debts and loans. |
Example #1:
-
Suppose you want to find your friends, who are called "Grace".
-
The command you would enter is
people find n/Grace. -
This requests Sharkie to list out the people with the name, "Grace".
-
Expected Outcome #1:
-
All your friends with the name, "Grace" will be listed out:
2 persons listed!
Example #2:
-
Suppose you want to find your friends with unsettled debt(s) or loan(s).
-
The command you would enter is
people find t/debt loan. -
This requests Sharkie to list out the people with unsettled debt(s) or loan(s).
-
Expected Outcome #2:
-
All your friends with unsettled debt(s) or loan(s) will be listed out:
2 persons listed!
Clearing all contacts : clear
Suppose you want to clear all the contacts in your contact list,
the command you would enter is our people clear command.
Format: people clear
Example:
-
Suppose you want to clear all your contacts.
-
The command you would enter is
people clear. -
This requests Sharkie to delete all the contacts in your contact list.
-
Expected Outcome:
-
Sharkie will delete all the contacts and return an empty contact list.
Contact list has been cleared!
Contributions to the Developer Guide
Given below are sections I contributed to the Developer Guide. They showcase my ability to write technical documentation and the technical depth of my contributions to the project. |
Design
Model component
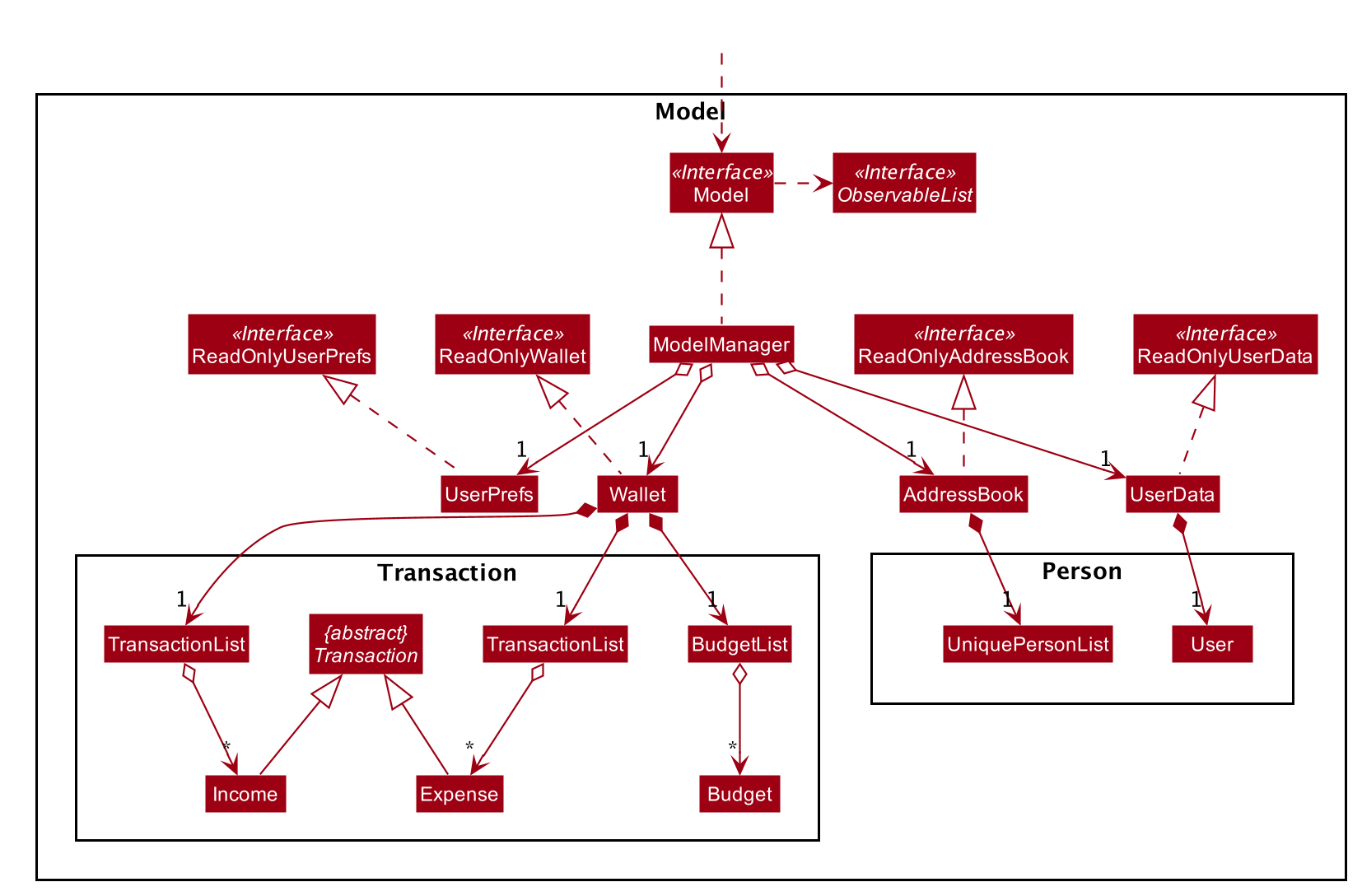
The ModelManager class diagram is drawn separately as it is too complicated to include all the details in the
Model component diagram.
|
API : Model.java
The Model,
-
stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. -
stores the Wallet data.
-
stores the Address Book data.
-
stores the User data.
-
exposes an unmodifiable
ObservableList<Person>and an unmodifiableObservableList<Transaction>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to these lists so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the respective lists change. -
does not depend on any of the other three components.
The Wallet,
-
consists of a
BudgetList. -
consists of a
TransactionList, which containsIncome(s) and aTransactionListwhich containsExpense(s).
The AddressBook,
-
consists of a
UniquePersonList.
The UserData,
-
consists of a
User.
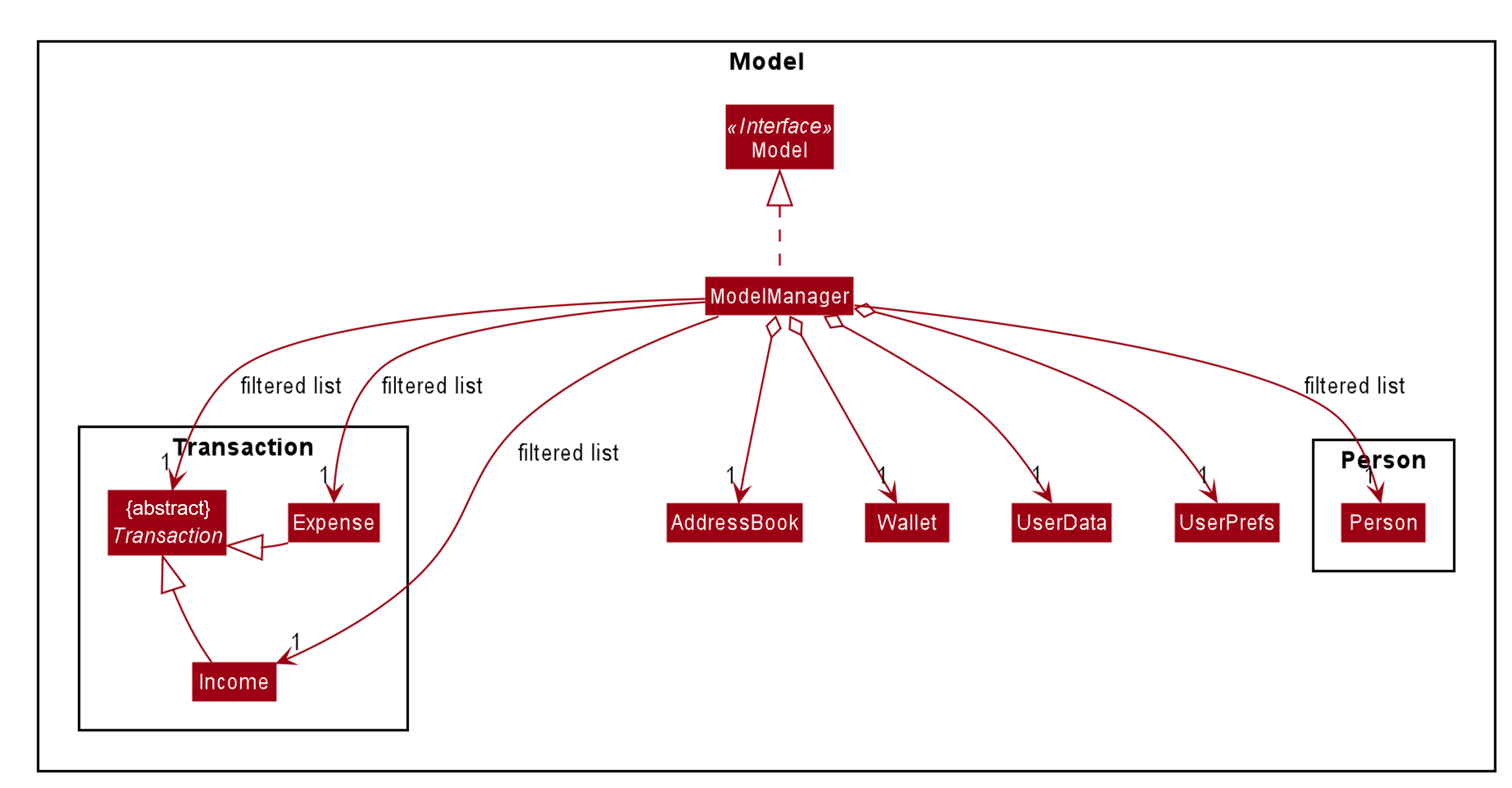
The Model package consists of four main packages: Person, Transaction, Reminder and Tag.
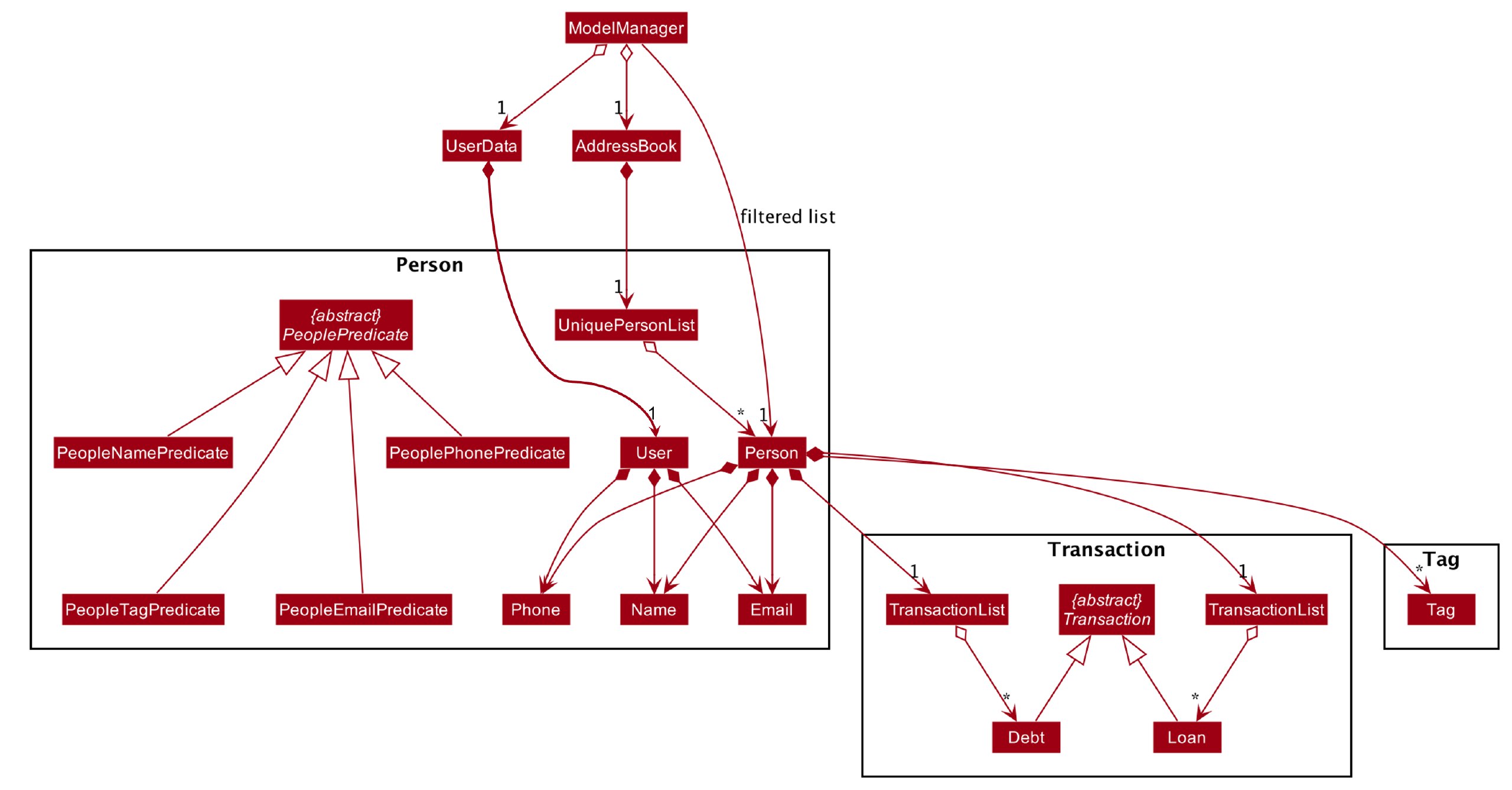
The diagram above shows how the Person package is implemented:
-
PeoplePredicate:PeopleNamePredicate,PeoplePhonePredicate,PeopleTagPredicate,PeopleEmailPredicateare implemented for the execution ofpeople findcommand. -
A
Userconsists of aName, aPhoneand anEmail. -
A
Personconsists of aName, aPhone, anEmail, aTransactionListofDebt(s), aTransactionListofLoan(s) and a set ofTag(s).
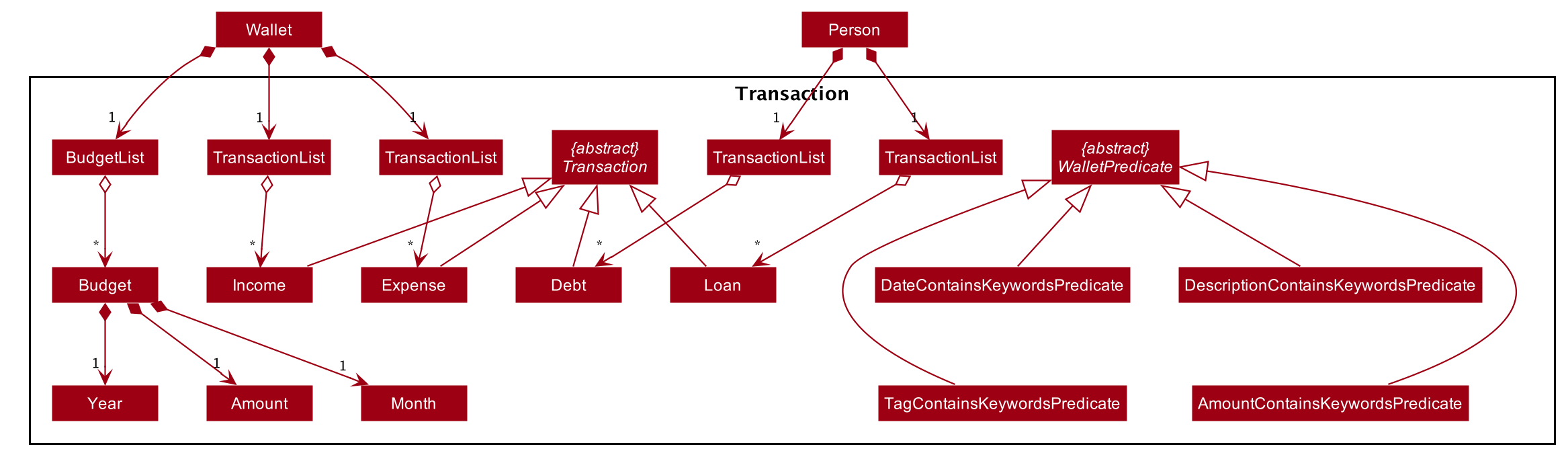
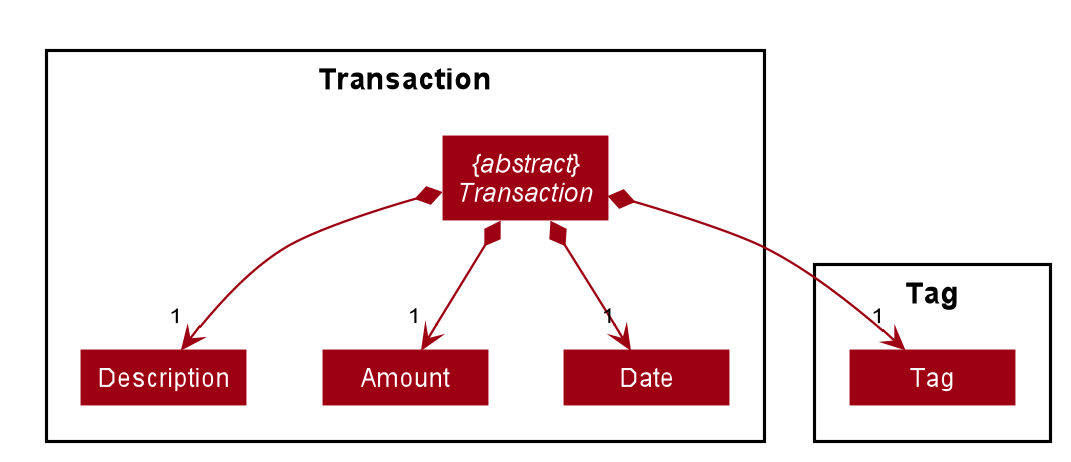
The association between Transaction and Amount is not shown in In-depth structure of Transaction package in the Model Component to keep the diagram less messy.
However, the association is shown in Transaction class diagram.
|
The diagram above shows how the Transaction package is implemented:
-
WalletPredicate:DateContainsKeywordsPredicate,DescriptionContainsKeywordsPredicate,TagContainsKeywordsPredicate,AmountContainsKeywordsPredicateare implemented for the execution ofwallet findcommand. -
The abstract class
Transactionis extended byIncome,Expense,DebtandLoan. ATransactionconsists of aDescription, anAmount, aDateand aTag. -
A
Budgetconsists of aYear, aMonthand anAmount.
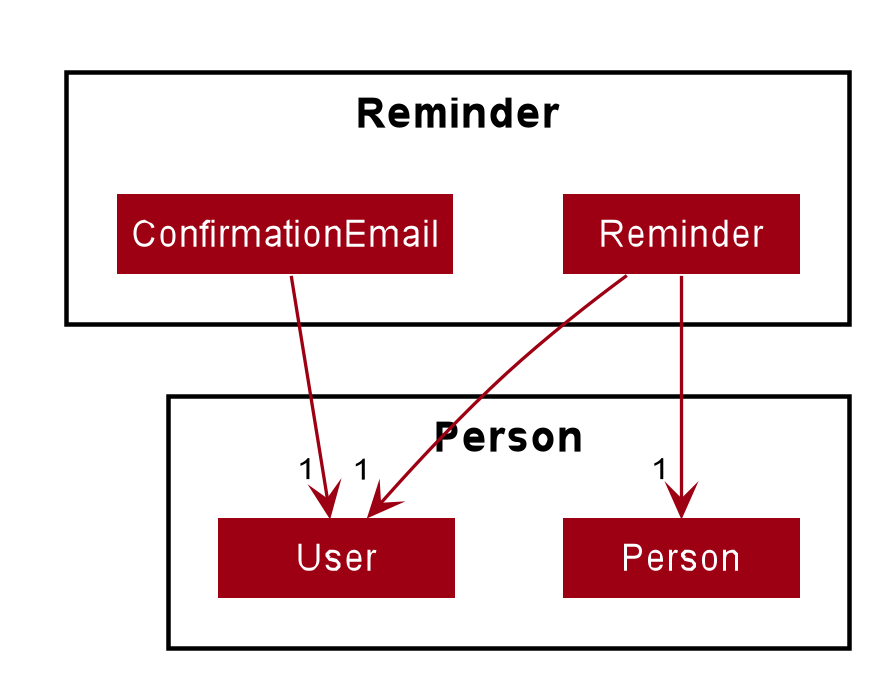
The Reminder package is implemented for Sharkie's reminder feature. The diagram above shows how the Reminder package is implemented:
-
The
Reminderconsists of aUser(the sender) and aPerson(the receiver).-
A
Reminderobject is created whenever thepeople remindorpeople remindallcommand is executed.
-
-
The
ConfirmationEmailconsists of aUser.-
The
ConfirmationEmailis implemented to validate the user’s email address during user’s first login to Sharkie.
-
The Tag package only consist of a class, Tag and it does not depend on other components in the Model.
Implementation
People Received Command
The people received command is implemented in the class, PeopleReceivedCommand.
This command can be accessed from Logic#execute(). It deletes the Loan(s) of the indicated Person
(the Person with the specified index in the Address Book).
The following activity diagram illustrates what happens when the user executes a people received command:
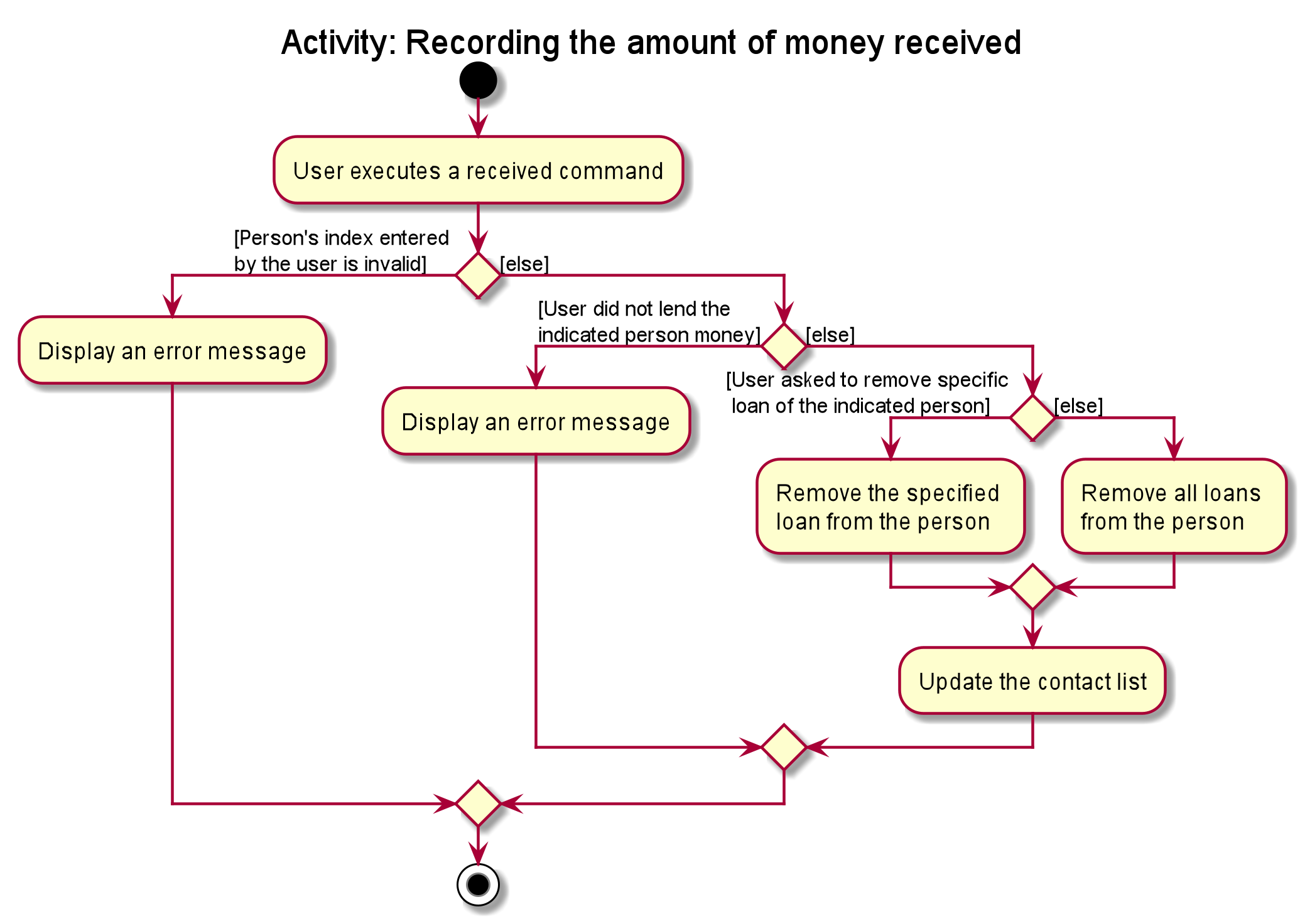
Implementation of people received command
-
In
PeopleReceivedCommandclass, the list ofPersonsis obtained from theModelviaModel#getFilteredPersonList()and the indicated person is extracted from the list. -
The list of
Loansof thePersonis extracted and modified based on the command entered by the user. -
A new
Personwith the modified list ofLoansis created. -
This new
Personreplace the initialPersonat the indicated index viaModel#setPerson()and thefilteredPersonsin theModelis updated.
The following sequence diagram summarizes what happens during the execution of a people received command:
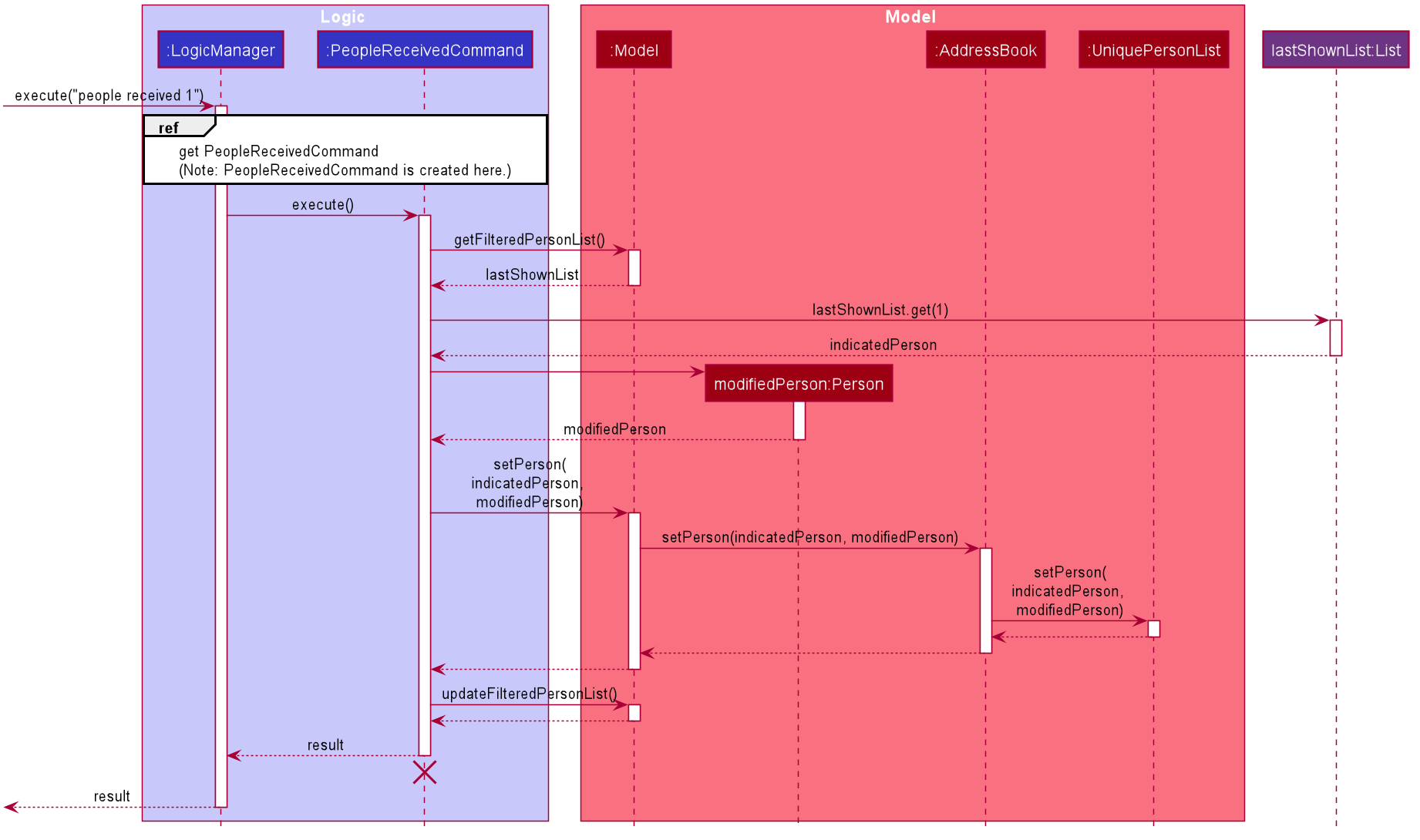
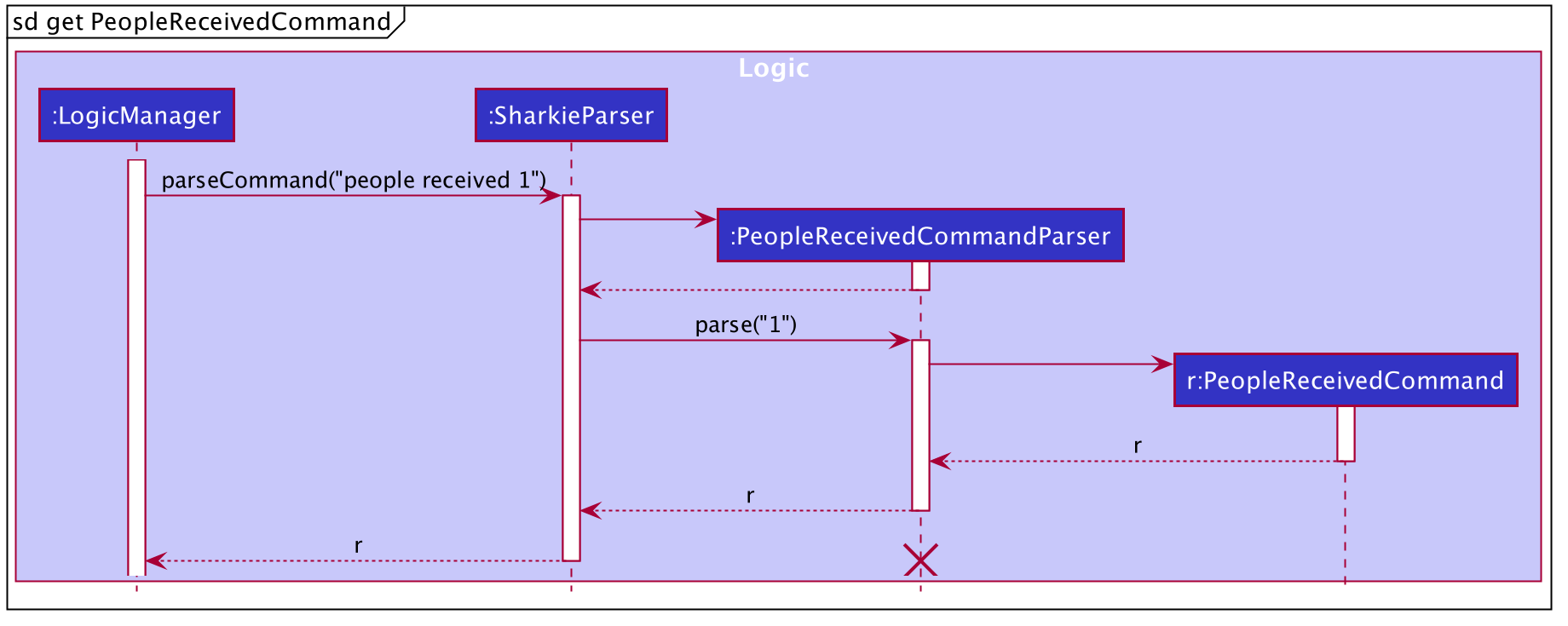
people received command
The lifeline for PeopleReceivedCommand and PeopleReceivedCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML,
the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
|
Design Considerations
Aspect: Deletion of Loan from the indicated person.
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Creates a new
Personwith the modified list ofLoansand useModel#setPerson()to replace the indicatedPersonwith the newPersoncreated.-
Pros: Preserve the immutable property of
Person. -
Cons: Have to copy over all the attribute values, such as
Name,Phoneand more.
-
-
Alternative 2: Modify the list of
Loansin the indicatedPersondirectly.-
Pros: Easier and can save time from copying the information from one
Personto another. -
Cons:
Personloses the immutable property.
-
Appendix C: Use Cases
Wallet Tab
(For all use cases below, the System is the Wallet and the Actor is the User, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC1 - Recording an expense
-
User requests to add an expense into the wallet.
-
Wallet adds the expense and displays the expense in the list of expenses.
Use case ends.
-
1a. The amount keyed in by the user is invalid.
-
1a1. Wallet shows an error message.
-
1a2. User re-enters the expense.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the amount keyed in by the user is correct.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: UC2 - Recording an income
MSS
-
User requests to add an income into the wallet.
-
Wallet adds the income and displays the income in the list of incomes.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The amount keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of recording an expense (UC1) are repeated until the amount keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC3 - Setting budget
MSS
-
User requests to set a budget.
-
Wallet sets the amount keyed in as the budget of the month indicated.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The amount keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of recording an expense (UC1) are repeated until the amount keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. The amount keyed in by the user has no date attached to it.
-
1b1. Wallet automatically assigns the budget entered as the default budget of each month.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: UC4 - Deleting a transaction
Preconditions: The transaction that the user wants to delete exists in the wallet.
MSS
-
User requests to delete a specific transaction in the wallet.
-
Wallet deletes the transaction and displays the list of remaining transactions.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The transaction’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
-
1a1. Wallet shows an error message.
-
1a2. User re-enters the index.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the index keyed in is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: UC5 - Editing a transaction
Preconditions: The transaction that the user wants to edit exists in the wallet.
MSS
-
User requests to edit a specific transaction in the wallet.
-
Wallet edits the transaction and shows the list with the edited transaction.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The transaction’s index keyed in by the is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of deleting an transaction (UC4) are repeated until the index keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. The user did not indicate the field to edit.
-
1b1. Wallet shows an error message.
-
1b2. User re-enters the edit command.
Steps 1b1-1b2 are repeated until the edit command keyed in is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: UC6 - Finding a transaction
MSS
-
User keys in a keyword.
-
Wallet lists out the transactions that contain the keyword.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The keyword entered by the user does not exist in the wallet.
-
1a1. Wallet shows an empty list.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: UC7 - Listing all transactions
MSS
-
User enters the list command.
-
Wallet lists out all the transactions.
Use case ends.
People Tab
(For all use cases below, the System is the Address Book and the Actor is the User, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: UC8 - Adding a person
MSS
-
User requests to add a person into the address book.
-
Address book adds the person and displays the person in the list of people.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s details keyed in by the user is invalid.
-
1a1. Address book shows an error message.
-
1a2. User re-enters the person’s details.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the details keyed in is correct.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: UC9 - Sending reminder to a friend
MSS
-
User requests to send a reminder to a friend.
-
Address book sends a reminder to the friend.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
-
1a1. Address book shows an error message.
-
1a2. User re-enters the index.
Steps 1a1-1a2 are repeated until the index keyed in is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
-
1b. Address book shows that the friend does not owe the user money.
Use case ends.
Use case: UC10 - Recording the money the user owes
Preconditions: The friend, who user owes exists in the address book.
MSS
-
User enters the amount borrowed from a friend.
-
Address book records the amount, which the user owes the friend.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of sending reminder to a friend (UC9) are repeated until index keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. The amount keyed in by the user is invalid.
-
1b1. Address book shows an error message.
-
1b2. User re-enters the amount.
Steps 1b1-1b2 are repeated until the amount keyed in is correct.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: UC11 - Recording the money the user lends
Preconditions: The friend, who user lends exists in the address book.
MSS
-
User enters the amount lent to a friend.
-
Address book records the amount, which the user lends to the friend.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of sending reminder to a friend (UC9) are repeated until the index keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. The amount keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1b1-1b2 of recording the money the user owes (UC10) are repeated until the amount keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC12 - Deleting a person
Preconditions: The person, who user wants to delete exists in the address book.
MSS
-
User requests to delete a specific person in the address book.
-
Address book deletes the person and shows the list of the remaining people.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of sending reminder to a friend (UC9) are repeated until the index keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC13 - Editing a person
Preconditions: The person, who user wants to edit exists in the address book.
MSS
-
User requests to edit a specific person in the address book.
-
Address book updates the indicated person’s detail and show the list of people with the edited person.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The person’s index keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of sending reminder to a friend (UC9) are repeated until the index keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
1b. The person’s new details keyed in by the user is invalid.
Steps 1a1-1a2 of adding a person (UC8) are repeated until the details keyed in by the user is valid.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: UC14 - Finding a person
MSS
-
User keys in a keyword.
-
Address book lists out the people, who contain the keyword in their names.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
1a. The keyword entered by the user does not exist in the address book.
-
1a1. Address book shows an empty list.
Use case ends.
-
Appendix G: Instructions for Manual Testing
Recording the flow of money
-
Recording the money you lend to a person
-
Prerequisites: The person whom you lend to exists in the person list.
-
Test case:
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/12.00
Expected: A loan named Dinner with $12.00 is added into the loan list of the first person. -
Test case:
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/12.00 d/02/02/2020
Expected: A loan named Dinner with $12.00, recorded under the date 02/02/2020 is added into the loan list of the first person. Total amount of money, which you lent to the first person is shown in the result display. -
Test case:
people lend 0 n/Dinner $/12.00
Expected: The loan is not recorded. Error details shown in the result display. -
Other invalid
people lendcommands to try:-
people lend, -
people lend 1, -
people lend 1 n/Chicken Rice, -
people lend 1 $/12.00, -
people lend n/Chicken Rice $/12.00, -
people lend x n/Dinner $/12.00(where x is larger than the person list size), -
people lend x n/Dinner $/12.00(where x is a negative number), -
people lend x n/Dinner $/12.00(where x is a non-integer), -
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/x(where x is a negative number), -
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/x(where x is greater 92233720368547758.07), -
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/x(where x has more than 2 decimal places) or -
people lend 1 n/Dinner $/x(where x is not a number).
Expected: Similar to previous
-
-
-
Recording the money you received from a person
-
Prerequisites: The person whom you received from exists in the person list.
-
Test case:
people received 1 i/1
Expected: The first loan of the first person is deleted from the loan list. Remaining amount of loan, which have yet settled by the first person is shown in the result display. -
Test case:
people received 0 i/1
Expected: No loan is deleted. Error details shown in the result display. -
Other invalid
people receivedcommands to try:-
people received, -
people received 1, -
people received i/1, -
people received x i/1(where x is larger than the person list size), -
people received x i/1(where x is a negative number), -
people received x i/1(where x is a non-integer value), -
people received 1 i/x(where x is larger than the loan list size), -
people received 1 i/x(where x is a negative number or zero) or -
people received 1 i/x(where x is a non-integer value)
Expected: Similar to previous
-
-
Sending reminders
-
Reminding a specific person about the unsettled loan(s).
-
Prerequisites: Connected to the Internet. Your firewall or antivirus programme (if any) allows the connection to STMP port 587. The person who you want to remind exists in the person list. The person has at least one loan in the loan list. The email of the person to be reminded is a valid email (You can generate an email from temp-mail.org).
-
Test case:
people remind 1
Expected: A reminder is sent to the first person’s email. A carbon copy (CC) of the reminder is sent to you. A success message shown in the result display. -
Test case:
people remind 0
Expected: No reminder is sent. Error details shown in the result display. -
Other invalid
people remindcommands to try:-
people remind, -
people remind x(where x is larger than the person list size), -
people remind x(where x is a negative number) or -
people remind x(where x is a non-integer value)
Expected: Similar to previous
-
-
-
Reminding all people about the unsettled loan(s).
-
Prerequisites: Connected to the Internet. Your firewall or antivirus programme (if any) allows the connection to STMP port 587. At least one person in the list has at least one loan. The email(s) of the people to be reminded are valid email(s) (You can generate an email from temp-mail.org).
-
Test case:
people remindall
Expected: A reminder is sent everyone, who has unsettled loan. A carbon copy (CC) of each of the reminder is sent to you. A list of people reminded is shown in the result display, along with the success message.
-